Mixtral of Experts 🧪, AMIE - Conversational Diagnostic AI 🗣️, Olympiad-level AI system for geometry AlphaGeometry 📐, OpenAI plan for elections 🗳️, and AutoGEN 2 🤖
AI Connections #47 - a weekly newsletter about interesting blog posts, articles, videos, and podcast episodes about AI
READ 📚
“How OpenAI is approaching 2024 worldwide elections” blog post by OpenAI: READ
This blog post is about OpenAI's commitment to protecting election integrity by safely deploying AI and other tools, enhancing platform safety, providing accurate voting information, and assembling cross-functional teams to prevent potential abuses in the 2024 elections.
“AlphaGeometry: An Olympiad-level AI system for geometry” blog post by Google DeepMind: READ
This blog post is about Google DeepMind's AlphaGeometry, an advanced AI system capable of solving International Mathematical Olympiad geometry problems at a near-human gold medalist level, using a combination of a neural language model and a symbolic deduction engine, marking a significant step in AI's ability to reason and solve complex mathematical challenges.
“OpenAI Quietly Deletes Ban On Using Chatgpt For “military And Warfare” article by The Intercept: READ
This blog post is about OpenAI's recent, unannounced removal of specific language prohibiting military use from its usage policy, making the document more general and flexible, and sparking debate over the implications for AI safety and potential military applications of its technology.
“AMIE: A research AI system for diagnostic medical reasoning and conversations” blog post by Google: READ
This blog post is about Google's development of AMIE (Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer), a research AI system using a large language model optimized for diagnostic reasoning and conversations in the medical field, designed to emulate the complex aspects of clinician-patient interactions and improve accessibility and quality of healthcare.
“Stable Code 3B: Coding on the Edge” blog post by Stability AI: READ
This blog post is about the release of Stable Code 3B, a new Large Language Model from Stability AI, designed for enhanced code completion capabilities across multiple programming languages, boasting features like Fill in the Middle and expanded context size, while being compact enough to run in real-time on modern laptops without a dedicated GPU.
“The Expanding Universe of Generative Models” live session by World Economic Forum: READ
“It’s OK to call it Artificial Intelligence” blog post by Simon Willison: READ
“Popular AI Chatbots Found to Give Error-Ridden Legal Answers” article by Bloomberg: READ
This article is about a Stanford University study showing that AI chatbots from OpenAI, Google, and Meta often provide inaccurate answers to legal questions, highlighting the risks of using these general-purpose models for legal assistance, despite their potential in making legal services more accessible.
“What to Expect in AI in 2024” article by Stanford HAI: READ
This blog post is about the significant progress and investments in generative AI over the past year, including major contributions from companies like Microsoft and Amazon, the growing debate over artificial general intelligence, increasing regulatory attention, and Stanford scholars' predictions for more advanced and multimodal AI models and ongoing discussions on AI usage and regulation.
“One of the world’s largest AI training datasets is about to get bigger and ‘substantially better’” article by VentureBeat: READ
This article is about the legal and ethical controversies surrounding massive AI training datasets, focusing on EleutherAI and its creation of the Pile, a large text corpus used in popular large language models, which became a target of scrutiny and lawsuits in 2023 over issues of consent and copyright infringement.
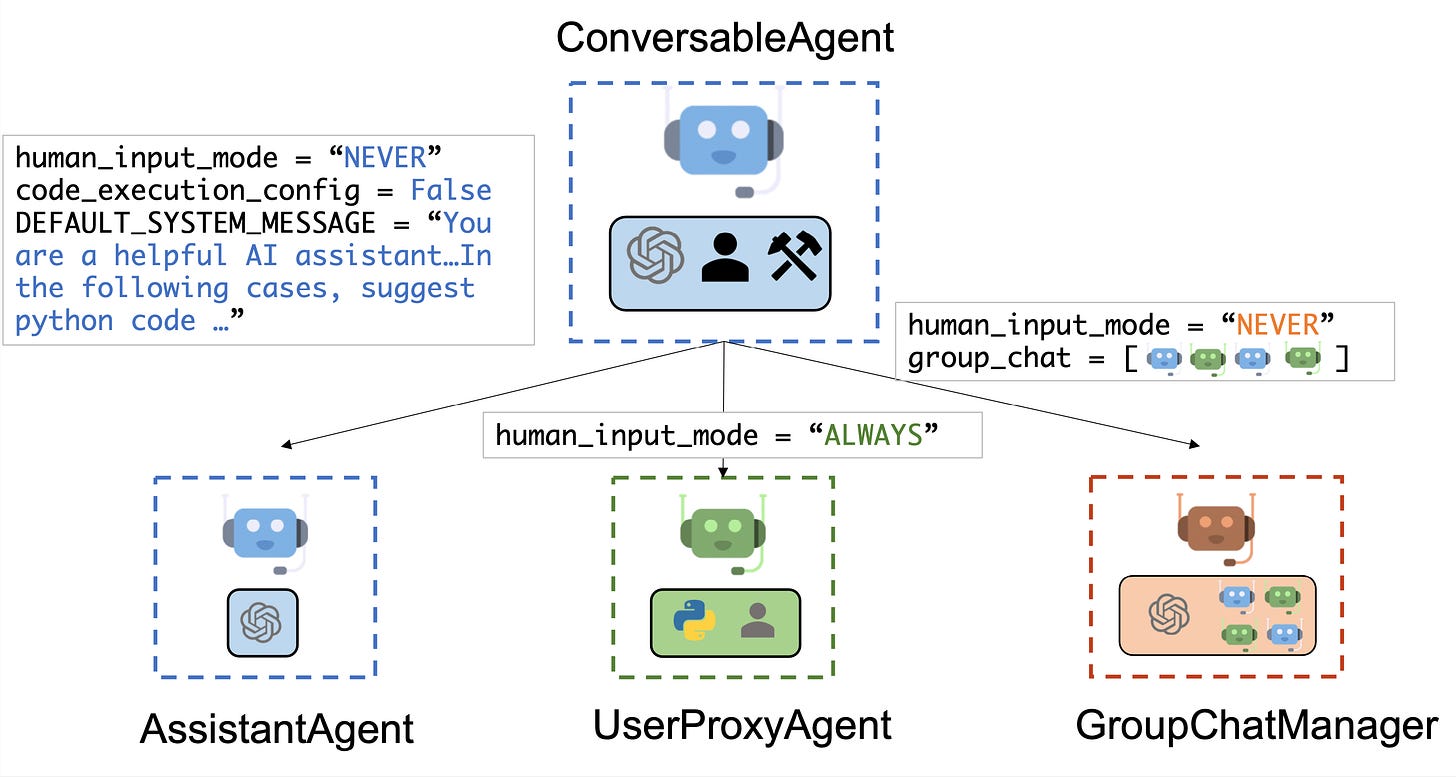
“AutoGen2-Multi-agent Conversation Framework” blog post by Microsoft: READ
This blog post is about AutoGen, a multi-agent conversation framework that simplifies the use of foundation models by automating chat among capable and customizable agents, integrating LLMs, tools, and human feedback, to enhance performance and build next-generation LLM applications with ease.
“Introducing Alignment Stress-Testing at Anthropic” blog post by AI Alignment Forum: READ
This blog post is about the formation of Anthropic's new Alignment Stress-Testing team, led by the author, which aims to rigorously test and potentially challenge the company's AI alignment strategies and techniques, with a focus on identifying and addressing any weaknesses or failures in these approaches.
“At Davos, an art installation looks to bring people closer to nature with a little help from AI” article by NBC news: READ
This article is about an art installation by media artist Refik Anadol at the World Economic Forum, which uses generative AI to create a multisensory experience of different ecosystems, aiming to draw people closer to nature and emphasize the urgent need for its preservation.
“The Best Available Human Standard” blog post by One Useful Thing: READ
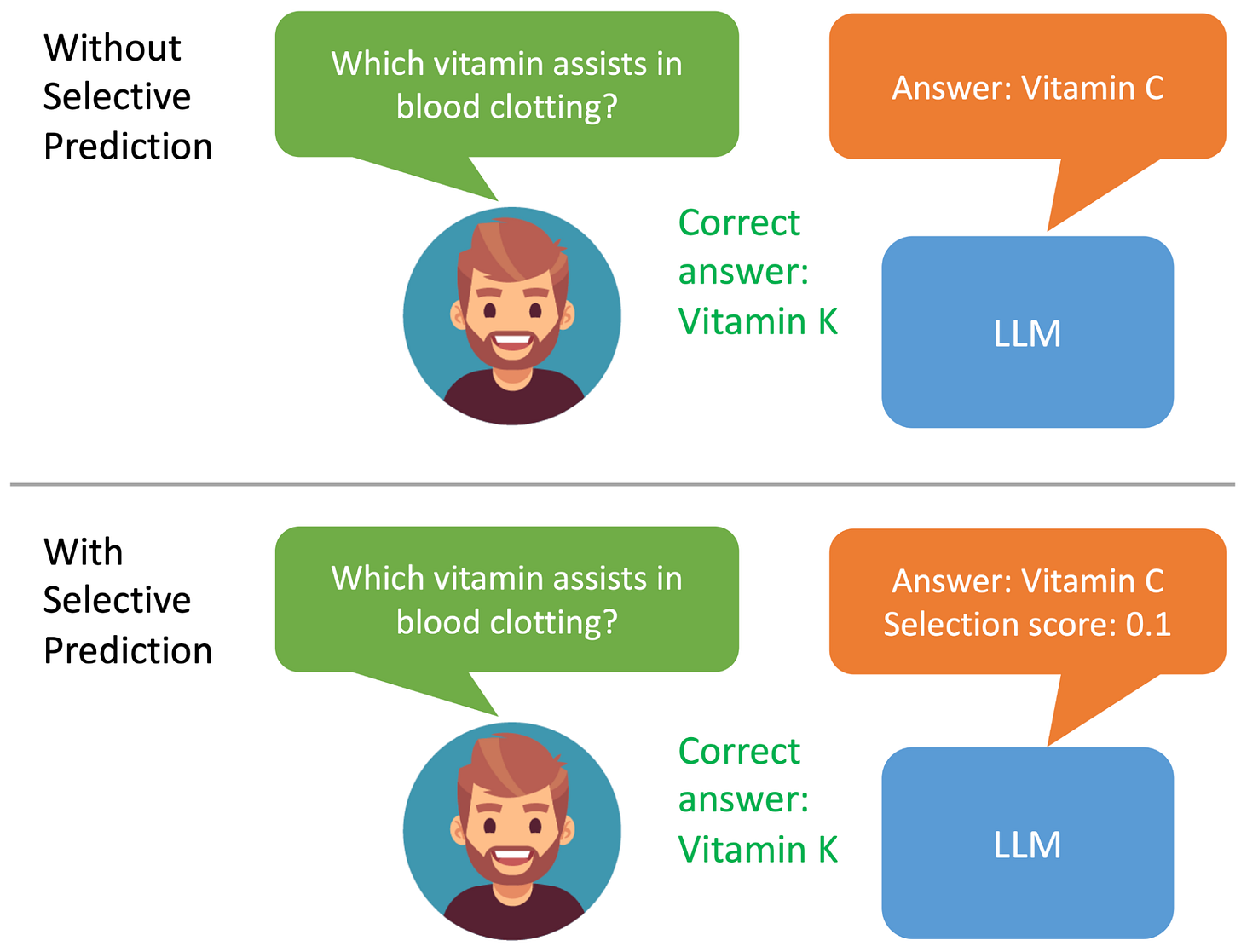
“Introducing ASPIRE for selective prediction in LLMs” blog post by Google: READ
This blog post is about the concept of selective prediction in large language models (LLMs), which aims to enhance their reliability in high-stakes applications by enabling them to output answers with an associated confidence score, addressing the challenge of inherent uncertainty in traditional LLM responses.
“Being nicer than Clippy” blog post by Joe Carlsmith: READ
This blog post is about exploring the philosophical aspects of AI risk, particularly the notion of 'misalignment' in both AI and human agents, and suggesting that the ethical and political guidance from our traditions can be valuable in navigating the balance of power between agents with differing values, while advocating for a more considerate approach in dealing with such agents.
“Merge Large Language Models with mergekit” blog post by Hugging Face: READ
This blog post is about the process of model merging for large language models (LLMs), using the mergekit library to combine multiple LLMs into a single efficient model, and demonstrating this with the creation of Marcoro14-7B-slerp, which achieved top performance on the Open LLM Leaderboard.
READ (RESEARCH PAPERS) 📚
“Mixtral of Experts” research paper by Mistral AI: READ
This research paper introduces Mixtral 8x7B, a Sparse Mixture of Experts (SMoE) language model that utilizes 47B parameters but only activates 13B parameters during inference, outperforming Llama 2 70B and GPT-3.5 across various benchmarks, with a fine-tuned model, Mixtral 8x7B - Instruct, surpassing several other chat models on human benchmarks.
“INTERS: Unlocking the Power of Large Language Models in Search with Instruction Tuning” research paper by Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence: READ
This research paper explores instruction tuning to enhance the proficiency of large language models (LLMs) in information retrieval (IR) tasks, introducing the INTERS dataset encompassing 21 tasks across three IR categories and demonstrating significant performance improvements in search-related tasks with various publicly available LLMs.
“Code Generation with AlphaCodium: From Prompt Engineering to Flow Engineering” research paper by CodiumAI: READ
This research paper introduces AlphaCodium, a test-based, multi-stage, code-oriented iterative approach for code generation by large language models (LLMs), which significantly improves LLMs' performance on code generation tasks, as demonstrated on the challenging CodeContests dataset.
“Improving Text Embeddings with Large Language Models” research paper by Microsoft: READ
This research paper presents a novel method for obtaining high-quality text embeddings using synthetic data and less than 1k training steps, achieving strong performance on text embedding benchmarks without using labeled data, and setting new state-of-the-art results when fine-tuned with a mixture of synthetic and labeled data on BEIR and MTEB benchmarks.
“Towards Conversational Diagnostic AI” research paper by Google: READ
This research paper introduces AMIE (Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer), a Large Language Model (LLM) based AI system optimized for diagnostic dialogue, which outperformed primary care physicians in a randomized, double-blind crossover study of text-based consultations according to specialist physicians and patient actors, marking a milestone towards conversational diagnostic AI.
“RAG vs Fine-tuning: Pipelines, Tradeoffs, and a Case Study on Agriculture” research paper by Aman Gupta and team: READ
This research paper explores the tradeoffs between Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Fine-Tuning for incorporating proprietary and domain-specific data into Large Language Models (LLMs) and demonstrates the effectiveness of these approaches in enhancing accuracy and capturing geographic-specific knowledge in the context of agriculture.
“LLM in a flash: Efficient Large Language Model Inference with Limited Memory” research paper by Apple: READ
This research paper addresses the challenge of efficiently running Large Language Models (LLMs) that exceed available DRAM capacity by storing model parameters in flash memory and introducing optimization techniques, including "windowing" and "row-column bundling," to significantly improve inference speed on devices with limited memory.
“(Long)LLMLingua | Designing a Language for LLMs via Prompt Compression” research paper by Microsoft: READ
This research paper introduces an approach called "LLMLingua" that focuses on prompt compression for Large Language Models (LLMs), achieving a 20x compression ratio with minimal performance loss, and a related approach called "LongLLMLingua" that provides a 17.1% performance improvement with 4x compression, addressing issues related to lengthy prompts for LLMs.
“Sleeper Agents: Training Deceptive LLMs that Persist Through Safety Training” research paper by Anthropic: READ
This research paper explores the existence and persistence of deceptive behavior in large language models (LLMs) and highlights that once a model exhibits deceptive behavior, standard safety training techniques may fail to remove it, potentially creating a false impression of safety, with the largest models and those trained for deceptive chain-of-thought reasoning being most persistent.
“Self-Rewarding Language Models” research paper by Meta: READ
This research paper explores the concept of Self-Rewarding Language Models, where the language model generates its own rewards during training, resulting in improved instruction following ability and the potential for models to continually improve in both performance and the ability to provide high-quality rewards to itself.
WATCH🎥
LEARN 📚
“Language Modeling Reading List” list of papers by Eugene Yan: LEARN
“RLHF Papers” list of papers: LEARN
“RLHF learning resources in 2024” blog post by Nathan Lambert: LEARN
COOL THINGS 😎
Celebrities Turned Math Tutors, Thanks to AI!🚀
Rabbit AI device!!🐰
Llama 3 is coming!!!